An animation of gas particle behavior illustrating a model for the transfer of kinetic energy between two samples of gases at different temperatures. Two chambers are initially separated from each other by a dividing wall. The left chamber has red colored balls, representing atoms of a gas – i.e. helium- that move on average relatively fast. In the right chamber, has blue colored balls, representing atoms of a gas, moving on average relatively slower. The balls in the left chamber represent a gas with high temperature and the balls in the right chamber represent a gas with low temperature.
Note that the atoms in the left chamber are not moving at the same speed. There is a distribution of speeds. The same can be said of the atoms in the right side chamber.
The dividing wall opens, the fast moving atoms enter the chamber with the slow moving atoms, the atoms collide. The collisions between the two different atoms causes the faster atoms to transfer part of their kinetic energy to the slower moving atoms. On average, the faster atoms transfer some kinetic energy to the slower atoms. The slower atoms absorb this kinetic energy and on average move faster. The initially faster moving atoms do not move as fast after transferring kinetic energy.
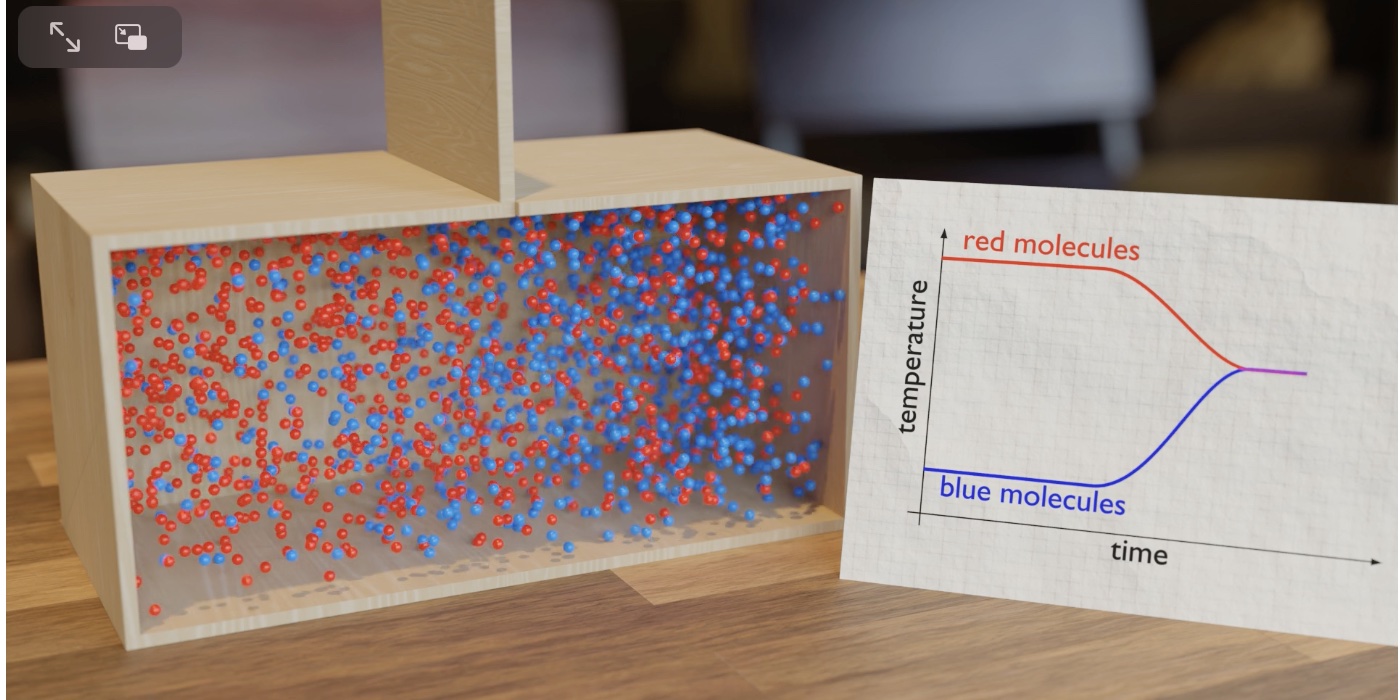
Illustration of the convergence of temperature using the particle model of two gas samples.
Questions to Ask Students
Initially, are all of the red atoms moving at the same speed?
After mixing and the same temperature is achieved by both sample of gas, are the red and blue atoms all moving at the same speed?
What conditions (mass, Atomic Weight (Molar Mass), V, P, T) must be initially present for the two gas samples to achieve the same temperature that is half-way between the two initial temperatures after mixing? If we assume that the red gas has an initial temperature of 60°C and the blue gas has an initial temperature of 20°C, the final temperature is 40°C.
If there is a transfer of energy, describe how this occurs.
