This simulation provides an opportunity to investigate several factors influencing the initial rate of a chemical reaction
A + B -> C
Variables that can be manipulated include concentration, temperature, surface area of the reactants and the addition of a catalyst during the simulation. Students interpret a simplified qualitative representation of the reaction by counting the initial and final number of particles of A, B and C and noting the time it takes for the reaction to be completed.
The resulting reaction rates are compared to the reaction rate of a specified reaction. The data are automatically plotted on a graph. Students can easily make qualitative observations about the relative rate of reaction.
The influence of concentration on rate of reaction - particle behavior - Animation.
Consider the simple reaction A + B -> C
Run the simulation "rate of reaction" AACT. Choose increase concentration, record your observations of the initial and final number of particles of A, B and C, as well as the time. Choose decrease concentration, record your observations.
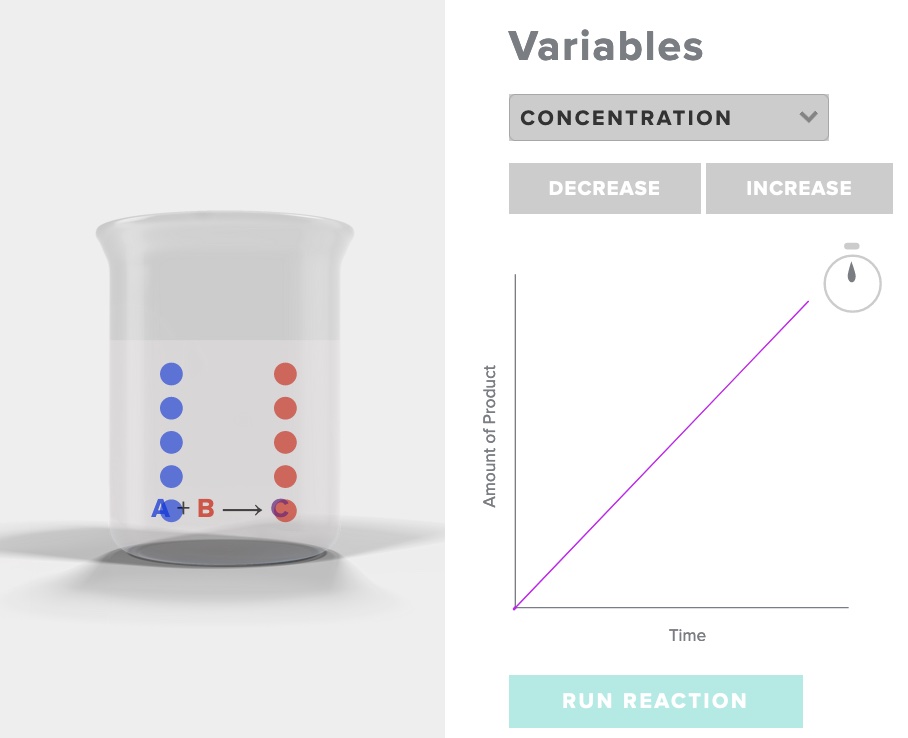
After interacting the the AACT simulation "Reaction Rates" explain why the rate of reaction is affected by a change in concentration with specific reference to the behavior of particles in three situations - concentration [A], concentration 1/2[A], and concentration 2[A].
This page is under construction. Web page author: T. Greenbowe, University of Oregon.
The influence of temperature on rate of reaction - particle behavior - Animation
Consider the simple reaction A + B -> C
Run the simulation "rate of reaction" AACT. Choose increase temperature, record your observations of the initial and final number of particles of A, B and C, as well as the time. Choose decrease temperature, record your observations.
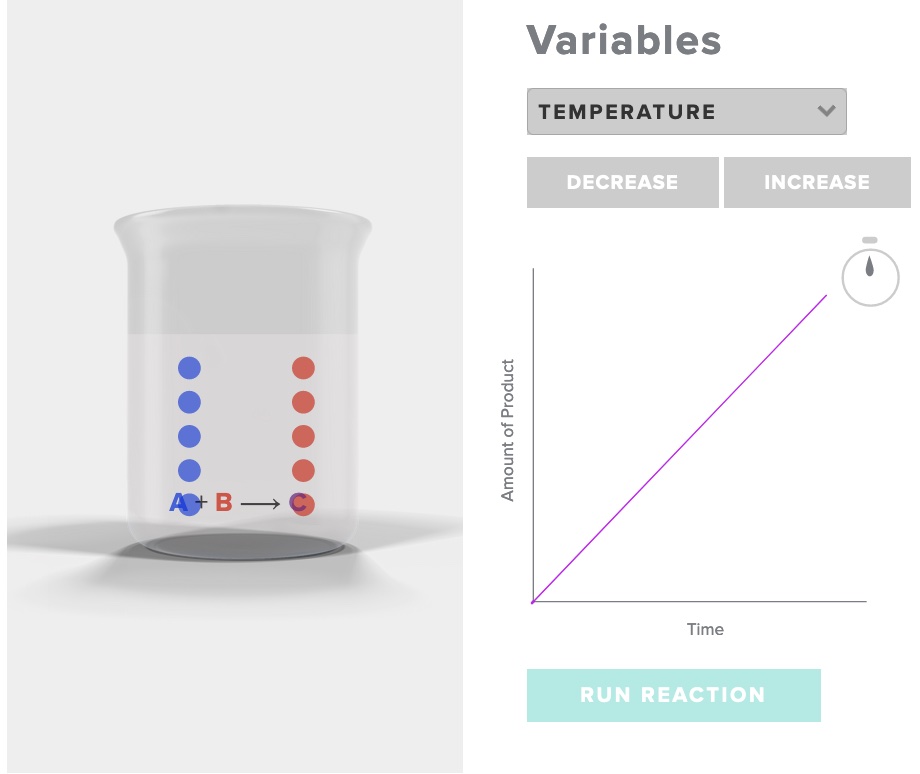
After interacting the the AACT simulation "Reaction Rates" explain why the rate of reaction is affected by a change in temperature with specific reference to the behavior of particles in three situations - temperature T1, temperature T2, and temperature T3,
